Adjectives have three types of degrees.
- Positive Degree
- Comparative Degree
- Superlative Degree
What is Positive degree? Example
The positive degree of an adjective is the adjective in its general form. It denotes the mere existence of some quality. It represents the basic quality of something without comparing it to anything else. It tells about the quality of a person, place, or thing.
For example,
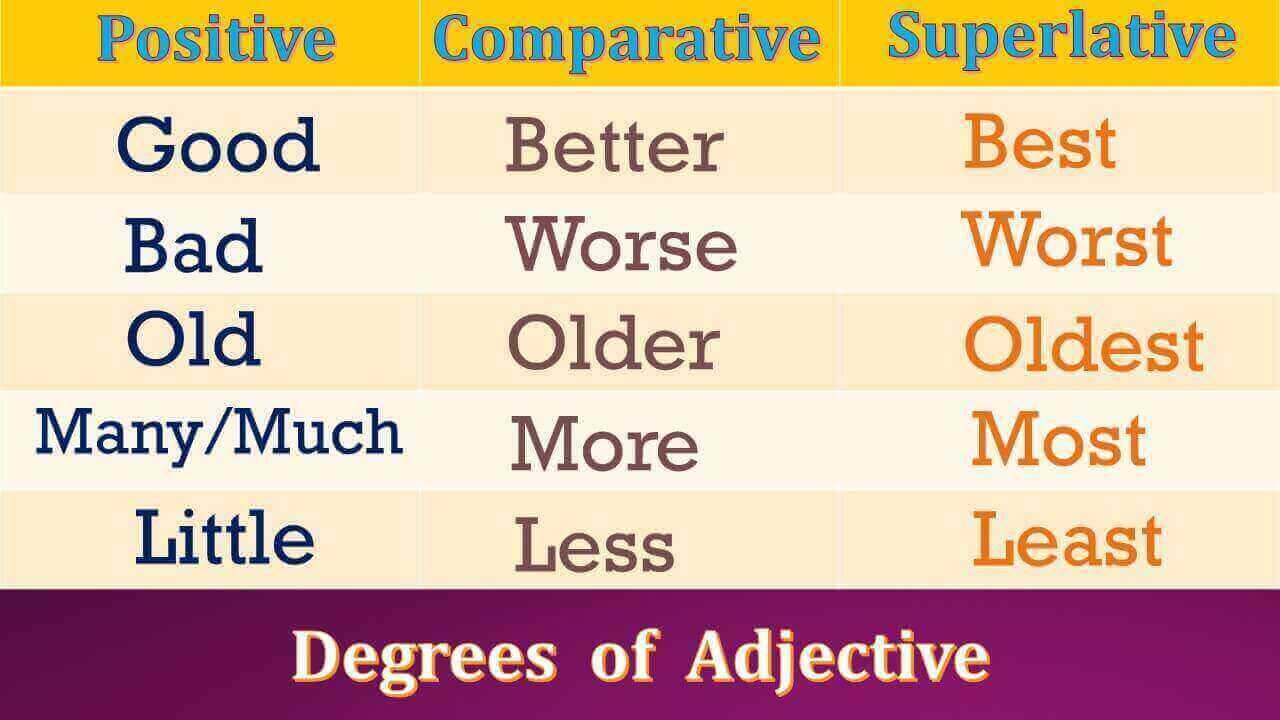
Good – Better – Best
High – Higher – Highest
Tall – Taller – Tallest
Beautiful – More beautiful – Most beautiful
Here, “good”, “high”, “tall” and “beautiful” are Positive degrees. These are used to tell about one person.
What is Comparative degree? Example
The comparative degree denotes a higher degree of quality than the positive. The comparative is used to compare two persons or things. Generally, it is formed by adding “-er” to the end of an adjective or by using “more” before the adjective.
For example,
Good – Better – Best
High – Higher – Highest
Tall – Taller – Tallest
Beautiful – More beautiful – Most beautiful
Here, “better”, “higher”, “taller” and “most beautiful” are Comparative degrees. These are used to compare two persons or things.
What is Superlative degree? Example
The Superlative degree denotes the highest degree of quality. It is used to compare more than two persons or things. Generally, it is formed by adding “-est” to the end of an adjective or by using “most” before the adjective.
For example,
Good – Better – Best
High – Higher – Highest
Tall – Taller – Tallest
Beautiful – More beautiful – Most beautiful
Here, “best”, “highest”, “tallest” and “most beautiful” are Superlative degrees. These are used to compare more than two persons or things.
Rules to form Comparative and Superlative Degrees of Adjectives
Rule – 1 :
The comparative degree of an adjective is formed by adding ‘er‘ and the superlative degree is formed by adding ‘est‘ to the positive degree.
Example :
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
| Tall | Taller | Tallest |
| Long | Longer | Longest |
| Strong | Stronger | Strongest |
| Great | Greater | Greatest |
| Clever | Cleverer | Cleverest |
Rule – 2 :
If the positive degree ends in ‘e‘, ‘r‘ is added to change it into a comparative degree, and ‘st‘ is added to change it into a superlative degree.
Example :
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
| Large | Larger | Largest |
| Wise | Wiser | Wisest |
| Safe | Safer | Safest |
| Fine | Finer | Finest |
Rule – 3 :
If the positive degree ends in a consonant and a vowel comes before it, the consonant is doubled. Then ‘er‘ and ‘est‘ are added to form comparative and superlative degree respectively.
Example :
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
| Big | Bigger | Biggest |
| Thin | Thinner | Thinnest |
| Sad | Sadder | Saddest |
| Hot | Hotter | Hottest |
Exceptions
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
| Deep | Deeper | Deepest |
| Cool | Cooler | Coolest |
Rule – 4 :
If a positive degree ends in ‘y‘ and a consonant is present before ‘y’. The ‘y’ is converted into ‘i’, and then ‘er’ and ‘est’ are added to form comparative and superlative degree respectively.
Example :
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
| Easy | Easier | Easiest |
| Happy | Happier | Happiest |
| Busy | Busier | Busiest |
| Heavy | Heavier | Heaviest |
Rule – 5 :
Adjectives of two syllables or more than two syllables form the Comparative and Superlative Degree by adding ‘more‘ and ‘most‘ before the Positive degree.
Example :
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
| Beautiful | More beautiful | Most beautiful |
| Important | More important | Most important |
| Difficult | More difficult | Most difficult |
| Intelligent | More intelligent | Most intelligent |
| Useful | More useful | Most useful |
Rule – 5 :
There are some adjectives. Their Comparative and Superlative degrees are different from Positive degrees.
Example :
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
| Good | Better | Best |
| Bad | Worse | Worst |
| Much | More | Most |
| Many | More | Most |
| Little | Less | Least |
FAQs
Q1. What is the superlative degree form of “good“?
The superlative degree of “Good” is “Best”. The comparative degree of “Good” is “Better”.
Good (Positive) – Better (Comparative) – Best (Superlative)
Q2. What is the comparative form of “lazy“?
The comparative degree of “Lazy” is “Lazier”. The superlative degree of “Lazy” is “Laziest”.
Lazy (Positive) – Lazier (Comparative) – Laziest (Superlative)
Q3. What is the comparative and superlative degree of “intelligent“?
The comparative degree of “Intelligent” is “More intelligent”. The superlative degree of “Intelligent” is “Most intelligent”.
Intelligent (Positive) – More intelligent (Comparative) – Most intelligent (Superlative)
Q4. What is the comparative of “old“?
The comparative degree of “Old” is “Older”. The superlative degree of “Old” is “Oldest”.
Old (Positive) – Older (Comparative) – Oldest (Superlative)
Q5. What is the superlative degree of “fast“?
The superlative degree of “Fast” is “Fastest”. The comparative degree of “Fast” is “Faster”.
Fast (Positive) – Faster (Comparative) – Fastest (Superlative)
Q6. What is the comparative degree of “colourful“?
The comparative degree of “Colourful” is “More colourful”. The superlative degree of “Colourful” is “Most colourful”.
Colourful (Positive) – More colourful (Comparative) – Most colourful (Superlative)
Q7. What is the comparative and superlative degree of “thin“?
The comparative degree of “Thin” is “Thinner”. The superlative degree of “Thin” is “Thinnest”.
Thin (Positive) – Thinner (Comparative) – Thinnest (Superlative)
Q8. What is the superlative degree of “pretty“?
The superlative degree of “Pretty” is “Prettiest”. The comparative degree of “Pretty” is “Prettier”.
Pretty (Positive) – Prettier (Comparative) – Prettiest (Superlative)
Q9. What is the comparative and superlative degree of “heavy“?
The comparative degree of “Heavy” is “Heavier”. The superlative degree of “Heavy” is “Heaviest”.
Heavy (Positive) – Heavier (Comparative) – Heaviest (Superlative)
Q10. What is the superlative form of “cheap“?
The superlative form of “Cheap” is “Cheapest”. The comparative degree of “Cheap” is “Cheaper”.
Cheap (Positive) – Cheaper (Comparative) – Cheapest (Superlative)
Q11. What is the comparative and superlative form of “comfortable“?
The comparative degree of “Comfortable” is “More comfortable”. The superlative degree of “Comfortable” is “Most comfortable”.
Comfortable (Positive) – More comfortable (Comparative) – Most comfortable (Superlative)
Q12. What is the comparative degree of “late“?
The comparative degree of “Late” is “Later”. The superlative degree of “Late” is “Latest”.
Late (Positive) – Later (Comparative) – Latest (Superlative)
Q13. What is the comparative and superlative form of “difficult“?
The comparative degree of “Difficult” is “More difficult”. The superlative degree of “Difficult” is “Most difficult”.
Difficult (Positive) – More difficult (Comparative) – Most difficult (Superlative)
Q14. What is the comparative and superlative degree of “big“?
The comparative degree of “Big” is “Bigger”. The superlative degree of “Big” is “Biggest”.
Big (Positive) – Bigger (Comparative) – Biggest (Superlative)
Related Contents :
1. Sentences
2. Singular and Plural Number
3. Gender in English Grammar
4. Strong verbs and Weak verbs